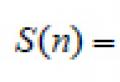Interest rate definition. Money market interest rate
And calculation of the parameters of this transaction.
The financial mathematics course consists of two sections: one-time payments and payment flows. One-time payments- these are financial transactions in which each party, when implementing the terms of the contract, pays the amount of money only once (either lends or repays the debt). Payment flows- these are financial transactions in which each party, when implementing the terms of the contract, makes at least one payment.
There are two parties involved in a financial transaction - the lender and the borrower. Each party can be either a bank or a client. The basic financial transaction is the lending of a certain amount of money. Money is not equivalent in relation to time. Modern money is usually more valuable than future money. The time value of money is reflected in the amount of accrued interest money and the pattern of its accrual and payment.
The mathematical apparatus for solving such problems is the concept of “percentage” and and .
Percentage - basic concepts
Percent- one hundredth of the pre-agreed base (that is, the base corresponds to 100%).
Examples:Answer: more
| original debt amount | |
| (days) | a fixed period of time to which the interest (discount) rate is tied (usually one year - 365, sometimes 360 days) |
| interest (discount) rate for the period | |
| debt term in days | |
| debt term in shares of the period | |
| amount of debt at the end of the term |
Interest rate
Interest rate- the relative amount of income for a fixed period of time. The ratio of income (interest money - the absolute amount of income from lending money) to the amount of debt.
Accrual period- this is the time interval to which the interest rate is dated; it should not be confused with the accrual period. Usually I take a year, half a year, quarter, month as such a period, but most often we deal with annual rates.
Interest capitalization- adding interest to the principal amount of debt.
Extension- the process of increasing the amount of money over time due to the addition of interest.
Discounting- inverse to the increase, in which the amount of money related to the future is reduced by the amount corresponding to the discount (discount).
The quantity is called the accumulation factor, and the quantity is called the discounting factor under the corresponding schemes.
Interest Rate InterpretationWith the scheme " simple interest"The initial basis for calculating interest throughout the entire term of the debt in each period of application of the interest rate is the original amount of the debt.
With the scheme " compound interest"(for integers) the initial base for calculating interest throughout the entire period in each period of application of the interest rate is the amount of debt accrued over the previous period.
Adding accrued interest money to the amount that serves as the basis for calculating it is called capitalization of interest (or reinvestment of the deposit). When applying the “compound interest” scheme, interest capitalization occurs at each period.
Interpretation of the discount rateWith the "simple interest" scheme ( simple discount) - the initial basis for calculating interest throughout the entire term of the debt at each period of application of the discount rate is the amount to be paid at the end of the deposit term.
With the “compound interest” scheme (for integers) ( complex discount) - the initial basis for calculating interest throughout the entire period in each period of application of the discount rate is the amount of debt at the end of each period.
Simple and complex interest rates
"Direct" formulas
| Simple interest | Compound interest | ||
| - interest rate | buildup | ||
| - interest rate |
discounting (banking accounting) |
"Reverse" formulas
| Simple interest | Compound interest | ||
| - interest rate | discounting (mathematical accounting) | ||
| - interest rate | buildup |
Variable interest rate and reinvestment of deposits
Let the debt term have stages whose length is equal to , ,
- with a simple interest scheme
1 . The contract provides for the accrual of a) simple, b) compound interest in the following order: in the first half of the year at an annual interest rate of 0.09, then next year the rate decreased by 0.01, and in the next two half-years increased by 0.005 in each of them . Find the amount of the increased deposit at the end of the term if the amount of the initial deposit is $800.
Market interest rate as the most important macroeconomic indicator
The interest rate is important. The interest rate is the charge for money lent. There were times when the law did not allow remuneration for the fact that unspent, borrowed money was lent. In the modern world, loans are widely used, for the use of which interest is set. Since interest rates measure the cost of using money by entrepreneurs and the reward for non-use of money by the consumer sector, the level of interest rates plays a significant role in the economy of the country as a whole.
Very often in economic literature the term "interest rate" is used, although there are many interest rates. Interest rate differentiation is related to the risk taken by the lender. The risk increases as the loan term increases, since the likelihood that the lender may need the money before the established date for repayment of the loan becomes higher, and the interest rate increases accordingly. It increases when a little-known entrepreneur applies for a loan. A small firm pays a higher interest rate than a large one. For consumers, interest rates also vary.
However, no matter how different interest rates are, they are all influenced by: if the supply of money decreases, then interest rates increase, and vice versa. That is why the consideration of all interest rates can be reduced to the study of the patterns of one interest rate and in the future we will use the term “interest rate”
Distinguish between nominal and real interest rates
Real interest rate determined taking into account the level. It is equal to the nominal interest rate, which is set under the influence of supply and demand, minus the inflation rate:
If, for example, a bank makes a loan and charges 15%, and the inflation rate is 10%, then the real interest rate is 5% (15% - 10%).
Interest calculation methods:
Simple interest rate
Simple interest growth chart

Determine the interest and the amount of accumulated debt if the simple interest rate is 20% per annum, the loan is equal to 700,000 rubles, the term is 4 years.
- I = 700,000 * 4 * 0.2 = 560,000 rub.
- S = 700,000 + 560,000 = 1,260,000 rub.
A situation where the loan term is less than the accrual period
The time base can be equal to:- 360 days. In this case we get ordinary or commercial interest.
- 365 or 366 days. Used for calculation exact percentage.
- The exact number of days of the loan is determined by counting the number of days between the date of the loan and the date of its repayment. The day of issue and the day of repayment are considered one day. The exact number of days between two dates can be determined from the table of serial numbers of days in the year.
- The approximate number of days of the loan is determined from the condition that any month is taken to be equal to 30 days.
- Exact interest with exact number of loan days (365/365)
- Ordinary interest with the exact number of days of loan (bank; 365/360). If the number of loan days exceeds 360, this method results in the amount of accrued interest being greater than the annual rate.
- Ordinary interest with an approximate number of days of loan (360/360). It is used in intermediate calculations, as it is not very accurate.

A loan in the amount of 1 million rubles was issued on January 20 until October 5 inclusive at 18% per annum. What amount must the debtor pay at the end of the term when simple interest is calculated? Calculate in three options for calculating simple interest.
First, let's determine the number of days of the loan: January 20 is the 20th day of the year, October 5 is the 278th day of the year. 278 - 20 = 258. Approximately - 255. January 30 - January 20 = 10. Month 8 multiplied by 30 days = 240. total: 240 + 10 + 5 = 255.
1. Exact interest with the exact number of days of loan (365/365)
- S = 1,000,000 * (1 + (258/365)*0.18) = 1,127,233 rub.
2. Ordinary interest with the exact number of days of loan (360/365)
- S = 1,000,000 * (1 + (258/360)*0.18 = 1,129,000 rub.
3. Ordinary interest with an approximate number of days of loan (360/360)
- S = 1,000,000 (1 + (255/360)*0.18 = 1,127,500 rub.
Variable rates
Loan agreements sometimes provide for interest rates that vary over time. If these are simple bets, then the amount accrued at the end of the term is determined as follows.
Interest rates are the amounts indicated in the percentage of loans that are paid by recipients of loan funds for their use in a certain time period (quarter, month, year, etc.). If we look at interest rates from the perspective of money, then their value is a store of value.
Interest rates - what are they and how do they work?
Interest rates are for transactions carried out with other credit institutions. Thanks to their discount rates, central banks are able to influence interest rates that are set in commercial banks, the exchange rate of national currencies, as well as the state inflation rate.
If interest rates decrease, business activity, as well as the inflation rate, increases.
And, conversely, when interest rates rise, business activity decreases, which leads to a decrease and increase in the exchange rate of the national currency.
Interest rate policy is perhaps one of the most important and at the same time quite complex regulatory instruments for the banking system. The basic principles for constructing a scale of such rates are based on the demand/supply of credit resources, the size of deposits, storage periods, inflation rates, etc.
What structure do interest rates have in the general sense?
Interest rates are that part of the profit that borrowers pay to lenders for borrowed funds (otherwise borrowed), defined as a certain “irrational form of prices” of borrowed funds (loan capital).
Loan funds, in turn, are a set of monetary capital that are provided on the basis of repayment for temporary use for a certain amount of payment, expressed as a percentage. Form of movement of loan capital.
There is such a thing as sources of interest rates, which are the surplus value generated during the process of productive use of loan funds.
The division of the profit that is obtained during the use of loans, into the interest assigned to the already loaned funds, and the profit itself, represents business income that goes to the borrowers and arises under the loan market.
Thus, % directly express the relationship between the lenders and borrowers themselves and act as certain interest rates.
Interest rates are determined according to the specific conditions for the use of credit funds and are the subject of credit and monetary regulation by Central Banks.
Let us immediately note that the value of such rates can contribute to either an OUTFLOW of money capital from domestic state money markets or, conversely, an INFLOW. For this reason, in such markets the mobility of funds is very high, and their direct movement between various government money capital markets is reflected in interest rates.
Thus, a technical tool that helps to equalize different national interest rates is interest arbitrage. But we note that in 2015, the movement of monetary capital is influenced not so much by this technical means as by fluctuations (jumps) in the exchange rate. Now let's look at the main types of interest rates.
Interest rates on loans. What is important to know?
Interest rates on loans are the payment for loans taken from banks. In other words, this is a payment to your credit institution for the use of its funds for a certain time, i.e. credit resources. As a result, interest rates on loans here are the price of the loan (the price of borrowed money), i.e. the amount of funds that borrowers agree to pay lenders for using their capital for their needs.
Interest rate, interest money, interest rate, interest rate, interest per annum, per annum, all these concepts are essentially the same phenomenon - an indicator of the credit price, which reflects the ratio “amount of interest / amount of loan”, i.e. interest on loans. This percentage, in turn, is the amount of income from lending funds.
All these concepts are closely related to the periods of accrual of interest on a loan, which is the period of time during which interest is accrued for the use of credit funds. As a rule, this is the period from the moment the loan is issued until its full repayment.
The amount of interest rates depends on the types of loans, their amount, intended purpose, period of use, sufficiency of ensuring the fulfillment of obligations under the Loan and Liquidity Agreements, the reputation of borrowers and their credit history, discount rates of National Banks, inflation levels and other factors.
The main types of interest rates on loans are:
- simple,
- complex (floating),
- short-term
- and long-term.
Let's take a closer look. Simple interest rates on loans have a clearly fixed value, stipulated in the contract; for example, in 2015, the size of such rates varies from 10.5% to 14.5% per annum.
Let us immediately note that banks have the right to charge loan interest only for the period of time during which the borrowers actually used the loan funds. To put it another way, interest on the loan should accrue as it is repaid only on the remaining, outstanding amount.
Borrowers pay interest on the loan along with a certain part (according to the payment schedule determined by the loan agreement) of the principal debts. In this case, loan interest is part of the full loan amount.
Among other things, interest rates on loans indirectly depend on the terms of the loan itself. So, for example, short-term loans, unlike long-term ones, are usually issued by banks at a higher interest rate. What explains this “inconsistency” in the percentage level? It's simple - the desire of lenders to receive maximum profits with minimal risk and minimal costs.
About interest rates on deposits
First, let's look at the basic concepts. What are bank deposits?
It is also necessary to draw your attention to the fact that with excessively high interest rates on deposits, some banking institutions are trying to hide their problems.
In other words, they are trying to attract funds at high rates in order to urgently close the “gap” in their balance sheet. If a bank offers you to open a deposit where interest rates are several times higher than the market average, then think carefully about whether you should trust it with your savings?
How do interest rates affect the Forex market?
As mentioned above, an increase in lending rates leads to an influx of foreign investors, thereby causing an increase in the exchange rate of the national currency and its appreciation. A decrease in discount rates makes it possible to make loans measured in national currency cheaper, but at the same time the mass of money in circulation grows and increases. For this reason, a decrease in the discount rate can lead to the national currency exchange rate starting to fall.
If, following a decrease in discount rates, there is also a slight fall in the exchange rate of the national currency, then, most likely, in the very near future we must expect its long-term growth, and this must be taken into account by those traders who open long-term transactions on Forex.
In addition, interest rates affect those whose trading is not limited only. This point is due to the use of leverage provided by brokers.
In other words, it is the same loan with a minimum period of use equal to one day. For example, you open an order for the EUR/USD pair in the amount of one lot. It turns out that you have EUR in stock, and to make a purchase you borrow USD.
If, for example, the discount rate for EUR is 1%, and for American currency 2.5%, then you will place your Euros at 1% per annum, and dollars, respectively, at 2.5%. For the final transfer of a position, the commission will be 1.5% per annum or, in terms of days, 0.0041% per day.
Interest rates and the impact of inflation on them
Russian
Cash card, Russian Card for receiving cash from a machine.
Money supply, Russian The total money supply that determines the national economy and is in circulation.
Monetary system, Russian
Russian Assets and liabilities that are expressed in a fixed monetary value, for example: bank account balances, trade debtors, loans and trade creditors.
Money and item lottery, Russian , see lottery.
Monetary Policy, Russian A set of measures in the field of money circulation and credit aimed at regulating economic growth, curbing inflation, ensuring employment and equalizing the balance of payments; serves as one of the most important methods of state intervention in the reproduction process.
Monetary regulation, Russian One of the main means of government influence on economic processes. d.-k.r. economy of the Russian Federation is carried out by the Bank of Russia. it determines the norms of required reserves, discount rates on loans, sets economic standards for commercial banks, and conducts transactions with securities. The Bank of Russia, in cooperation with the government of the Russian Federation, develops and implements a unified state monetary policy aimed at protecting and ensuring the stability of the ruble.
Cash reward, Russian Reward in cash.
Money disaggio, Russian Deviation of the exchange rate of securities, stock values or banknotes downward compared to their nominal value. Disaggio is usually expressed as a percentage of the face value.
Monetary allowance, Russian Type of material support for military personnel established by the state. d.d. regulated by the Federal Law of the Russian Federation dated May 27, 1998 No. 76-FZ “on the status of military personnel” and other regulations. the circle of persons entitled to dd has been established. composition d.d. consists of
Monetary measurement, Russian End-to-end measurement of the results of business transactions using money, ensuring comparable results.
Cash support, Russian
Cash support, Russian A form of loan security that consists of maintaining a reserve fund from which payments can be made in the event of losses and claims by investors.
Money circulation, Russian
Monetary obligation, Russian The obligation of one party to pay money to the other party on the basis of an agreement, as a result of causing harm, and for other reasons. see also the order of repayment of claims under a monetary obligation.
Cash cover, Russian The degree to which a company has the cash security necessary to make all payments on time.
Cash allowance, Russian
- Cash benefits
Directly, Russian Directly, directly, first hand. prot. from second (fifth, tenth) hands. , myself
To determine the amount of loan interest, use the indicator norms percent(interest rates), which is considered as the ratio of the annual income on the loaned value to its absolute value.
The dynamics of the average interest rate (average interest rate) is determined by the relationship between supply and demand of loan capital in the market. The level of interest rate for each specific loan also depends on many factors.
The interest rate can be classified according to various criteria.
The relative quantitative expression of loan interest is the interest rate, and the absolute expression is percentage numbers (interest income)
Types of interest rates:
Depending on inflation: nominal and real
Depending on the possibility of changes: fixed and floating
Depending on the calculation method: simple and complex
Depending on the cost of interbank resources: LIBOR; LIBID, MIBOR; CYBOR; MIBID; KIBID
Depending on the types and terms of loans:
Short term, medium term and long term;
Deposit;
Discount;
Mortgage;
Credit
Depending on the loan form:
commercial
banking
consumer
Depending on the calculation methods, the official NBU rates:
rediscounting;
refinancing
1. Distinguish between real And nominal and effective interest rates.
Nominal interest rate - this is the current market interest rate. Real rate - this is the interest rate adjusted for inflation, that is, expressed in constant prices. It is the real rate that determines decisions about the feasibility (or inexpediency) of investments.
I. Fisher defined the nominal interest rate as a function of the real interest rate and the expected inflation rate:
where I is the nominal or market interest rate
g-real percentage value
e is the inflation rate.
Only in those cases when there is no price increase in the money market (e = 0), the real and nominal rates coincide.
Effective interest rate - the real profit that receive from one invested monetary unit for the whole year.
2. Fixed and floating interest rates. If the rate remains unchanged throughout the loan term, it is called fixed.
Floating interest rates(changing during the term of the loan agreement) are applied not only on the national, but also on the international loan capital market. The floating interest rate changes depending on fluctuations in interest rates in the capital market. Interest rates in Ukraine are currently quite high. This is explained by a number of factors influencing their value.
Expanding demand for loans in order to obtain additional means of payment to pay debt obligations. Uncertainty about the economic outlook reduces interest in raising funds on a long-term basis (by issuing shares and bonds) and increases the demand for short-term loans;
Monetary and credit policy of the NBU, aimed at curbing the growth of the money supply, which means a reduction in the supply of loan capital;
The state budget deficit, to cover which the government and local authorities, turning to the loan capital market, increase the demand for it.
3. According to the calculation method, interest rates can be simple or complex. Simple interest is accrued on the same amount throughout the year, complex interest is calculated taking into account the amount of accrued interest for the previous period. The accrued payment amount (S) for the calculation of simple interest consists of the sum of two elements - the amount of the original debt (P) and the amount of interest (I).
Formula for calculating simple interest:
S=R+I=R + Rni =R(1 + in),
where i is the interest rate (in fractions of units)
n - number of full years (ni\12 - number of months; ni| 360/365 number of days);
(1 + ni) - growth factor Formula for calculating compound interest:
S= P +I= P(1 +i)",
where (1 + i)" is the growth multiplier (interest capitalization factor).
In global banking practice, the following indicators of loan days are used when calculating interest:
The approximate number of days of each month (the duration of each month is assumed to be 30 days);
The exact number of days of the month (28,29, 30, 31 days).
The time base for calculating interest is determined as follows:
Exact interest: based on the actual length of the year - 365 or 366 days;
Ordinary interest: approximate interest based on the length of the year - 360 days.
Depending on the use of an approximate or exact period for calculating interest, German, French and English methods are distinguished.
English: exact number of days in each month and exact percentages
French: the exact number of days in each month and ordinary interest
German: p approximate number of days in a month and ordinary interest
Depending on the types and duration of loans.
The interest rate depends on the loan term. When determining the interest rate, the term of the loan is first taken into account. This is explained by the fact that increasing the term of a loan increases the risk of non-repayment due to changes in the external environment and financial condition of the borrower, and the risk of lost profits as a result of fluctuations in interest rates in the credit market. In this regard, interest rates are differentiated for short-term (up to one year), medium-term (from 1 to 5 years), long-term (over 5 years) loans.
The interest rate depends on the size of the loans. This is explained by the fact that with large loan amounts, the risk increases, the magnitude of which is estimated by the size of the lender’s loss due to the borrower’s insolvency. The probability of simultaneous bankruptcy of several borrowers is much less than of one of them. Consequently, the lender's risk is reduced when making loans to multiple borrowers. Servicing small borrowers results in relatively high bank costs. In this regard, depending on the size of the loans, the interest rate is differentiated for small, medium and large loans.
The interest rate depends on the security of the loan. Determine the interest rate on an unsecured (blank) loan. These loans are expensive because they involve increased risk. The interest rate is lower for loans that have the following collateral: “promissory note”, against receivables, against securities.
The purpose of using a loan can be different, and depending on it, the interest rate will also be different. Loans issued to eliminate financial difficulties, for the implementation of investment projects, etc. have an increased risk.
The interest rate is differentiated depending on the form of the loan(commercial, banking, government, consumer, etc.), as well as from the borrower (loan for commercial and industrial companies, agricultural, utility enterprises, individual borrowers).
Official interest rate May be:
- Byrediscounting ( rediscounting of securities, including bills of exchange);
- Byrefinancing (lending to banking institutions by the Central Bank);
- accounting NBU rate. The NBU discount rate is a monetary instrument with which it sets a benchmark for monetary market entities to determine the cost of attracted and placed funds for a certain period.
Depending on the cost of interbank resources. In connection with the development of interbank credit, interbank lending interest rates have become widespread. In world practice, an example of an interbank rate is the London one - LIBOR, which is used as the base rate when calculating the cost of individual international transactions. As a rule, a certain premium (margin) is added to the base LIBOR rate, which depends on the type of transaction, the financial situation of the borrower, and conditions on the loan capital market.
In Ukraine, the interbank rate is formed under the influence of supply and demand in the interbank market and increases depending on the state of the credit market. Thus, since mid-1994, the KIBOR and KIBID rates have been used as indicators of the interbank resources market.
KIBOR (from English - KievInterBankOfferedRate - offer for sale) represents the average rate on the interbank market for the placement of loans.
KIBID (from the English KievInterBankOfferedBid - offer to purchase) is the average announced rate for attracting loans. At this rate, banks are ready to buy an interbank loan.
The foundation of interest rate policy is the monetary policy of the state, pursued by the central bank (NBU in Ukraine). It focuses on the state of the economy and the free credit market. However, commercial bank rates are influenced by factors not directly related to central bank policy. In other words, there is a multifactorial process in which all components are in close interaction.
Monetary policy is one of the leading factors in changing interest rates in the credit market
By influencing the general conditions of credit supply, Central banks of all countries, through their policies, have a very significant impact on the level of the market price of credit resources - interest rates.
Monetary policy is a set of activities and government in the field of money circulation and credit.
Central bank monetary policy (monetary policy)- this is a set of government measures that regulate the activities of the monetary system, the loan capital market, order in order to achieve a number of general economic goals: stabilization of prices, rates, strengthening of the monetary unit.
Monetary policy is the most important element.
All impacts are reflected in the value of the total social product and.
The main goals of the state's monetary policy:- Containment
- Security
- Tempo regulation
- Mitigation of cyclical fluctuations in the economy
- Ensuring the stability of the balance of payments
Principles of monetary and credit regulation of the economy
Monetary regulation of the economy is carried out on the basis of the principle compensation regulation, which assumes the following:
- monetary policy restrictions, which involves limiting credit transactions by increasing the norms for reserving funds for participants in ; level up; restrictions on the growth rate in circulation compared to the commodity mass;
- monetary policy expansion, which involves stimulating credit operations; reduction of reserve standards for subjects of the credit system; falling lending rates; acceleration of currency turnover.

Monetary Policy Instruments
The development and implementation of monetary policy is the most important function. It has the ability to influence the volume of money supply in the country, which in turn allows it to regulate the level of production and employment.
The main instruments of the central bank in implementing monetary policy:- Regulation of official reserve requirements
It is a powerful means of influencing the money supply. The amount of reserves (part of the banking assets that any commercial bank is required to keep in the accounts of the central bank) largely determines its lending capabilities. Lending is possible if the bank has enough funds in excess of the reserve. Thus, increasing or decreasing reserve requirements can regulate the lending activity of banks and accordingly influence the supply of money.
- Open Market Operations
The main instrument for regulating the supply of money is the purchase and sale of government securities by the Central Bank. When selling and purchasing securities, the Central Bank tries to influence the volume of liquid funds of commercial banks by offering favorable interest rates. By purchasing securities on the open market, he increases the reserves of commercial banks, thereby contributing to an increase in lending and, accordingly, an increase in the money supply. The sale of securities by the Central Bank leads to the opposite consequences. - Regulation of the discount interest rate (discount policy)
Traditionally, the Central Bank provides loans to commercial banks. The interest rate at which these loans are issued is called the discount rate. By changing the discount interest rate, the central bank influences banks' reserves, expanding or reducing their ability to lend to the population and enterprises.
Factors that influence demand, supply and interest rates can be collectively called “monetary policy instruments.” These include:
Interest rate policy of the Bank of Russia
The Central Bank sets minimum interest rates for transactions it carries out. The refinancing rate is the rate at which loans are provided by commercial banks, or it is the rate at which bills of exchange are rediscounted from them.
The Bank of Russia may establish one or more for various types of transactions or pursue an interest rate policy without fixing the interest rate. Bank of Russia uses interest rate policy to influence market interest rates in order to strengthen the ruble.
Bank of Russia regulates the total volume of loans issued to them in accordance with the accepted guidelines of the unified state monetary policy, using the discount rate as an instrument. Bank of Russia interest rates represent the minimum rates at which the Bank of Russia carries out its operations.
Interest rate policy of credit institutions, being part of the national monetary policy, has a significant impact on the development and its stability. are usually free to choose specific rates on loans and deposits and use certain indicators reflecting the state of the short-term money market as guidelines when implementing interest rate policy. On the other hand, the central bank, in the targeting process, sets intermediate monetary policy goals that it can influence, as well as specific tools for achieving them. This may be the refinancing rate or interest rates on central bank operations, on the basis of which the short-term interbank lending rate is formed, etc.
The problems of identifying factors influencing the interest rate policy of commercial banks have worried specialists since the formation of economic theory. However, answers to many questions have not yet been found. Modern research aimed at identifying optimal rules for implementing national monetary policy is largely based on.
Methods of direct and indirect regulation of national monetary policy are considered in theory and practice. From the point of view of interest rate policy in the narrow sense (rates on credit and deposit operations, the spread between them), the instrument of its direct regulation is establishment by the central bank of interest rates on loans and deposits of commercial banks, indirect instruments - establishing the refinancing rate and the rate for central bank operations in the money and open markets.
Interest rates on loans and deposits as instruments of direct regulation are not often used in world practice. For example, the People's Bank of China sets rates that are considered indicative for the banking system. At the same time, the bank's policy is aimed at reducing the spread, which in the first half of 2006 was 3.65%, and by the end of 2009 - 3.06%, which indicates sufficient liquidity of the Chinese banking system.
In many countries, including Russia, the refinancing rate has become more of an indicative indicator, giving the economy only an approximate benchmark for the value of the national currency in the medium term, because it remains unchanged for a long time, while real rates in the money market change every day.
Required reserve standards
According to existing legislation, commercial banks are required to transfer part of the raised funds to special accounts in.
Since January 2004 established by the Central Bank following amounts of contributions to the mandatory reserve fund Bank of Russia: for ruble accounts of legal entities and foreign currency of citizens and legal entities, as well as for ruble accounts of citizens - 3.5%.
The maximum amount of deductions, i.e., required reserve standards, is 20% and cannot change by more than 5% at a time.
This standard allows the Bank of Russia to regulate the liquidity of the banking sector.
Reserves serve as a current regulation of liquidity in the money market, on the one hand, and as a limiter on the emission of credit money, on the other.
In case of violation of required reserve standards, the Bank of Russia has the right to indisputably collect from the credit institution the amount of funds not deposited, as well as a fine in the established amount, but not more than double.
Open market operations
Open market operations, which mean the purchase and sale by the Bank of Russia of corporate securities, short-term transactions with securities with the completion of a reverse transaction later. The limit on open market operations is approved by the board of directors.
In accordance with the law of July 10, 2002 No. 86-FZ (as amended on October 27, 2008) “On the Central Bank of the Russian Federation (Bank of Russia),” the Bank of Russia has the right to buy and sell goods of commercial origin with a maturity date of not more than 6 months, buy and sell bonds, certificates of deposit and other securities with a maturity of no more than 1 year.
Refinancing
Refinancing means lending by the Bank of Russia to banks, including accounting and rediscounting of bills. The forms, procedure and conditions of refinancing are established by the Bank of Russia.
Refinancing of banks is carried out by providing intraday loans, overnight loans and holding pawnshop credit auctions for a period of up to 7 calendar days.
Currency regulation
It should be considered from two sides. On the one hand, the Central Bank must monitor the legality of foreign exchange transactions, and on the other hand, monitor changes in the national monetary unit in relation to other currencies, avoiding significant fluctuations.
One of the methods of influencing the exchange rate is through central banks carrying out foreign exchange interventions or monetary policy.
Currency intervention is the sale or purchase by the Central Bank of foreign currency for the purpose of influencing the exchange rate and the total demand and supply of money. These obviously include transactions for the purchase and sale of precious metals on the domestic market of the Russian Federation, the procedure for which is regulated by letter of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation dated December 30, 1996 No. 390.
The main objectives of exchange rate policy in Russia are strengthening confidence in the national currency and replenishing gold and foreign exchange reserves. Currently, the monetary base is fully backed by gold and foreign exchange reserves.
Direct quantitative restrictions
Direct quantitative restrictions of the Bank of Russia include the establishment of limits on the refinancing of banks and the conduct of certain banking operations by credit institutions. The Bank of Russia has the right to apply direct quantitative restrictions in exceptional cases in order to implement a unified state monetary policy only after consultations with the government of the Russian Federation.
Benchmarks for growth of money supply indicators
The Bank of Russia can set growth targets for one or more indicators based on the main directions of the unified state monetary policy. In Russia, the main aggregate is the monetary aggregate.
Today, the monetary policy of central banks is guided by monetarist principles, where the Central Bank is tasked with strictly controlling the money supply, ensuring a stable, constant and long-term growth rate of the amount of money in the economy, equal to the growth rate of GDP.
Other factors influencing demand, supply and interest rates include:
- the situation in the real sector of the economy;
- return on investment in production;
- the situation in other sectors of the financial market;
- economic expectations of business entities;
- the need of banks and other business entities for funds to maintain their liquidity.
The politics of cheap and expensive money
Depending on the economic situation in the country, the central bank pursues a policy of cheap or expensive money.
Cheap money policy
Characteristic of a situation of economic recession and high level. Its goal is to make credit money cheaper, thereby increasing aggregate spending, investment, production and employment.
To implement a cheap money policy, the central bank can reduce the interest rate on loans to commercial banks or make purchases on the open market or reduce the reserve requirement ratio, which would increase the money supply multiplier.
Dear money policy
It is carried out with the aim of reducing the pace by reducing total expenditures and limiting the money supply.
Includes the following activities:- Increasing the interest rate. Commercial banks begin to take less loans from the Central Bank, therefore the supply of money is reduced.
- Sale by the central bank of government securities.
- Increase in reserve requirements. This will reduce excess reserves of commercial banks and reduce the money supply multiplier.
All of the above monetary policy instruments related to indirect (economic) methods of influence. In addition to these general methods of monetary regulation, the central bank also uses direct (administrative) methods designed to regulate specific types of credit. For example, a direct limitation on the size of bank loans for consumer needs.
Monetary policy has pros and cons. Strengths include speed and flexibility, less dependence on political pressure than fiscal policy. Problems in the implementation of monetary policy are created by cyclical asymmetry. The effectiveness of monetary policy may also decrease as a result of counter-directional changes in the velocity of money.