What the piston consists of. Tuning pistons, what are they made of, what are they
Pistons must withstand very high temperatures and high pressures for all four cycles. Pistons experience high loads, especially in boosted and racing engines. Turbo-charged engines with mechanical superchargers or nitrous oxide injection are more demanding on the strength of the piston. Add to this the possibility of an explosion, and you ask too much from these slugs. With a high engine boost, where the task is to achieve maximum power, the use of cast pistons is not enough. All piston parts are shown in the figure below.
Video - Piston Production Technology
Star cranks and ignition order for internal combustion engines
For crankshaft engines, the crankshaft has a number of elbows equal to the number of cylinders. The question arises about the angular arrangement of these elbows. Given that each elbow defines a plane, the projection of these planes onto a plane perpendicular to the axis of the crankshaft leads to the appearance of some straight lines intersecting even in the axial projection of the axis. We call this geometric structure a star crank.For example, the piston of a diesel engine.
Piston production
Typically, OEM pistons are made from a eutectic alloy that provides casting accuracy and have a high silica composition. Such pistons are much stronger and more stable than ordinary cast ones and their application is possible up to about 400 horsepower.
The next ignition, considered in the cylinder, occurs only after the crankshaft rotates with an angle, and the crank corresponding to this cylinder is in the same ignition position as the cylinder. The length between the two cranks, which successively reach the ignition position, must be equal to the angle between the two ignitions.
Building components of the white handle mechanism
It consists of: piston, bolt, segments. The force created by gas pressure. Turns the cylinder into normal reactions due to the shaft. Seals the cylinder in both directions. Evaporates part of the heat generated by burning fuel. In addition, it performs the following functions.
Forged pistons have a more sophisticated manufacturing technology, but also have better characteristics. In a first step, a piece of the hot aluminum alloy is forged and then machined to shape. The piston billet falls on the CNC machine, after which a high-precision part is obtained. Forged pistons are more expensive mainly due to the large amount of waste and processing on the CNC machine.
Creates directional movement of gases in a cylinder. Contains partially or fully a combustion chamber. Figure 3 shows the main areas of the piston. As a result of the high temperatures recorded on the piston, the following phenomena occur. The mechanical resistance of the piston material is reduced. When using aluminum alloys, the elastic modulus can be reduced by half in the area of \u200b\u200bthe piston surface.
Oils can undergo chemical transformations that turn them into lakes, and as a result, the phenomenon of compaction in their piston bodies occurs. This leads to a compromise of the cylinder roller. Uneven dilatation, depending on temperature and material distribution in different parts of the piston.
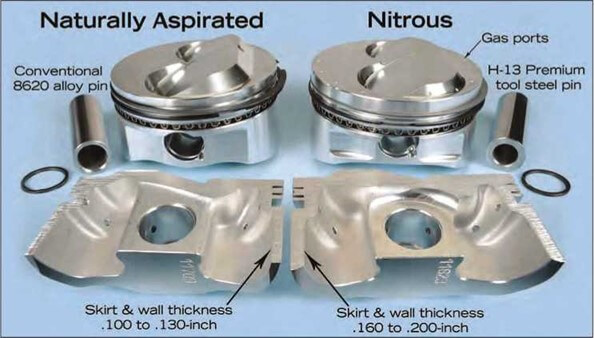
These mock-ups show the thickness of the piston metal for a turbo charge (left) and for nitrous oxide injection (right)
The construction of an engine designed for a high compression ratio or the use of pressurization involves the use of forged pistons that can better withstand high temperatures and high pressures.
Thermomechanical stresses are powerless. Piston construction. The design of the piston is based on its functional role, working conditions, technological capabilities, costs and the material used. The architecture of the piston head is based on the type of engine, as shown in the figure.
Figure 3 Head architecture. Solution a is simply technological and leads to a minimal heat exchange surface. The reverse side of the combustion chamber is made in the piston. Its shape takes into account the direction of the flow of fuel sent by the injector, and the need for organized movement of the motor fluid.
Vertical gas openings
These small, vertical holes at the bottom of the piston along the entire perimeter allow pressure to penetrate beyond the first compression ring when the fuel mixture is combusted. This increases the tightness of the combustion chamber but also increases the wear of the ring (pressure strongly presses the ring against the cylinder walls). During operation, in addition to the working stroke, the first compression ring is subjected to normal pressure, as in a conventional piston and, accordingly, lower friction force, in fact in these modes there is no need to strongly press the ring against the cylinder.
The piston head profile takes into account the need to evacuate heat obtained without thermal charging too much of the first compression segment, also called the fire segment. The architecture of the piston shell takes into account the actual operating conditions. There is no contact on the rest of the zone, and therefore a side cover of the piston shell is used to reduce friction.
Folding allows thermal expansion without reaching the piston grip or locking in the cylinder. In some pistons, in order to reduce the thermal load of the piston, it is possible to make cuts in T or in. It increases the elasticity of the jacket, but increases the thermal load of the piston head.

Such piston schemes are often used in drag racing.
Due to the pressure in the stroke mode, the vertical openings allow the upper compression ring to be pressed against the cylinder to ensure better tightness.
Lateral gas openings in grooves of rings
Functions performed by segments. Sealing the combustion chamber in dynamic conditions. Lubricating the piston-cylinder connection with the used lubricating oil. Segments are made in the form of split rings, as can be seen in the figure. The space between the ends is named.
The shape of the segment depends on its condition. Segment before and after a walk. Two or more compression segments and one or two lubricant / scraper segments are provided on one piston. The first compression segment is also called the fire site. Lubricating and scraper segments have the task of controlling the lubricating oil excessively on the cylinder mirror.
These very shallow recesses are made in the upper part of the groove of the upper piston ring around the entire circumference of the piston, which allows the ring to be pressed with gases to the lower plane of the groove of the piston ring and thereby increase the tightness.
This type is often used in circuit racing.
Small grooves from the upper ring to the bottom edge of the piston-flame belt.
Dynamic compaction with segments. To seal a segment, it must provide contact contact with the cylinder mirror as a result of its initial elastic deflection. Ensuring its tightness is ensured by the ability to move freely in the radial and axial directions. To do this, between the piston and the segmented channels there are racing and axle steering assemblies.
Under the action of forces due to pressure, elasticity, friction and inertia, the segment moves and develops contact pressures that allow it to perform the compaction function, assuming deformations and deviations from the nominal shape of the piston cylinder components. It is noteworthy that over time, wear and tear are also compensated due to the elasticity of the segment.

Coarse grooves, some make a barely visible flame belt.
Some pistons have a series of narrow grooves applied around the piston between the first compression ring and the piston bottom edge. These recesses are made to reduce the contact area with the cylinder when the piston is at top or bottom dead center. Also, these grooves are used to extinguish the flame on the approach to the ring.
Threading is not complete. The existence of joints does not allow this. Segments behave like a series of sycans, which gases that try to pass through a piston and cylinder meet them on their way. Figure 6 shows this process by observing how the highest pressure drop occurs at the fire segment level.
Figure 6 Pressure drop across the compression segment assembly. Gases that pass through the sealing system reach the place where they must be evacuated. In order not to pollute the environment, and since these gases usually contain fuel, they are again introduced into the intake manifold of the engine.
Expansion groove

Compensation groove is made on the jumper between the compression rings. This recess creates an additional volume for gases that have burst through the first ring, thereby reducing the pressure between the rings and this ensures less oscillation of the first ring, it is better kept at the bottom of its groove while maintaining the tightness of the combustion chamber.
Lubricating segments - cleaning. As indicated by their names, these segments process lubricating oil on a cylinder mirror. They are built in two ways. With its own elasticity. Expander segments. Their shape is conceived regarding the shape of their place on the piston. Constructive forms of lubricating segments.
Figure 8 shows how to start excess lubricating oil on the cylinder mirror. Figure 9 shows the segments of the lubricant - a scraper with an expander. These types of segments increase efficiency and durability. It is made of scraper elements and an elastic element, which ensures the constancy of radial contact pressure even in conditions of more pronounced wear.
Also see the following materials design features
When boring a block and installing pistons in a cylinder block, it is required to follow the recommendations of the piston manufacturer regarding cylinder processing, assembly and installation of cylinder piston parts. Basic information is printed on the top of the piston. If any information is not indicated by the piston manufacturer, either on the packaging or on the piston itself, then follow the recommendations of the car manufacturer. The symbols and meanings are explained below.
The shape of the elastic element depends on the manufacturer. The bolt is an element of a white crank mechanism that provides transmission of piston and ball forces in conditions of their relative rotation. Bolt mounting options. Loose in white and secured to the piston shoulder.
Loose at the piston shoulder and fastened in white. Loose at piston shoulder and in white. The latter option is the most common, as in this case, the bolt performs, intermittently, complete rotation around its axis, which is important to ensure uniform wear.
The bolt should provide a large force transmission, but in itself does not contribute to an increase in inertial forces, given that it moves with the same acceleration with the piston. It is made of alloy steels with sufficient mechanical strength. The rate of pressure increase in the cylinder during high combustion can be considered as a shock shock. Therefore, the core of the bolt must be tenacious, and the outer surface is made with high hardness in order to wear out as hard as possible. To achieve this, the bolts are wound superficially and then straightened without centers.
Information on top.
- Piston size. Some piston manufacturers apply the size of the piston in hundredths of a millimeter on the piston bottom; this control parameter allows you to check the piston manufacturing quality and dimensional accuracy before direct installation. For example: 83.93. This means that at the measured points the size of the piston does not exceed the specified size (taking into account the tolerance field). Measurement should be carried out at the piston temperature (+20 degrees), using a micrometer or similar measuring instrument, with an accuracy of up to one hundredth of a millimeter (0.01 mm).
- Mounting clearance. In order to ensure the sealing of the working cavity of the cylinder and the minimum work of the piston friction, as well as to prevent the hot piston from jamming, an assembly (temperature) gap is provided between the piston and the cylinder wall (Sp). With an increased gap between the piston and the cylinder wall, the engine operation deteriorates noticeably - there is a breakthrough of gases in the engine crankcase, the quality of the oil deteriorates, the rings coke and the engine power decreases. The size of this gap is set by the piston manufacturer for the initial temperature of the parts of the cylinder-piston group (usually +20 degrees), and depends mainly on the difference in temperature, piston mass and material properties of the contacting parts. Example: Sp \u003d 0.04. This means that the gap between the piston (according to the maximum size of the piston skirt) and the cylinder should be 0.04 mm (taking into account the tolerance field).
- Trademark. Every major piston manufacturer labels their products with their own brand name. Firstly, this is part of the fight against counterfeiting of their products, and secondly, having dismantled an old piston during repair, it immediately becomes possible to identify it using the casting number on the piston bottom.
- Installation direction. The pistons of modern engines have a strictly defined position in the engine, in particular, this is due to the fact that the axis of the piston pin has a certain offset, relative to the central axis of symmetry of the piston. This is done to reduce noise when the engine is running, or rather shock loads on the cylinder walls when shifting the piston in the extreme position. As a rule, manufacturers use two methods of depicting the installation direction– (for engines placed in front and behind the car). On the bottom, either an arrow is indicated indicating the direction of the front of the car (direction of movement), or a crankshaft with a flywheel is schematically depicted.
The casting number on the inside of the piston.
To ensure radial movement, one of the following measures is taken. Place two soft metal bolts on the bolt side. Elastic inner rings are provided in the channels practiced at the piston arms. Bottle lubrication can be performed centrally, under pressure, from a mustache or by leaking oil droplets as a result of inflation.
If the bolt is fixed on white, lubrication should be done only in the piston shoulder, since there is only a relative shield. To fix the bolt, the small shaft head is divided by milling. Conical holes made, one pass and one.
Experienced motorists often encounter difficulty in their work when a very old car comes in for repair, and there is no way to accurately identify the type of engine. Often there is simply incorrect information in the documents on the car, for example, an error (typo) in the VIN code or in the column “ENGINE TYPE”. But you need to repair, and you need to choose the right repair pistons.
Then information about the casting number on the inside of the piston comes to the rescue. It is necessary to remove the piston from the cylinder block, clean the internal cavity from carbon deposits and read the cast numbers and letters. This method is not suitable for all pistons, but the main suppliers of conveyors of European cars MAHLE, Kolbenschmidt, AE, Nural allow you to decrypt this data.
What is the "casting number"? Pistons having the same basic parameters are manufactured on the same technological equipment (in particular, in the same injection mold), then they are subjected to subsequent machining, depending on the required repair size and modification. That is, for pistons having STD and repair sizes, the numbers of the castings are the same. As a rule, several pistons per engine correspond to one casting number; this is a standard piston and its subsequent repairs. But there are exceptions (when the casting number coincides with several modifications of the piston) then it is necessary to measure the controlled geometric parameters.
How to decrypt? We recommend checking your casting numbers through paper catalogs of the respective manufacturers. In addition, you can decrypt this data using the on-line catalogs of our suppliers.
This is a component of the white crank mechanism connecting the piston bolt to the crankshaft spindle. Force forces due to gas pressure and inertia between the boot and mane. Figure 12 shows a bar drawing that distinguishes the following domains. Parts of the shaft. Component parts depend on general decisions made at the engine level.
The shaft rod is made in the form of a tube having a perpendicular axis on the axis of the rod. This can be divided or independent of the selected suture solution. If the bolt is loose in the leg, insert an intermediate bracket made by the Bronze Rule to improve cutting conditions.
It is necessary to identify the manufacturer of the old piston by trade marking, and then, using its catalog (paper or electronic), enter the number found. The value of the casting number must be entered directly in the search field by part number (Artikel #) or search by replacement number (Reference No :). Do not forget to check the results by the basic geometric size with old parts.
Lubrication in this area is provided either by centralization or by mixing oil droplets from the mist formed by the bubbles through specially controlled openings. To facilitate the movement of oil between the bushing and the bolt, screw channels are used.
White is usually performed by stamping in a closed mold, which provides high productivity in terms of obtaining high mechanical strength. The design of this component monitors how the crankshaft is made. If the crankshaft is made of one part, the bellows head is made with an assembled cover with screws or studs.