Water for cottage villages and houses. Autonomous water supply of the cottage village
When it comes to the water supply of private houses, then everything is not so simple. Especially if it is not a separate cottage or cottage, but the whole village. With a large number of houses, the load on the water supply system increases, and therefore the equipment will be more complicated.
Cottage Village Water Supply Project
Any construction and other work associated with it begins with the preparation of the project. As for water supply cottage village, then his project will differ both in the amount of equipment used and in the branching network.
In the simplest systems, water is supplied to residents by means of submersible pumps submerged in wells, with manual or automatic control.
In more complex cases, water is transported to storage tanks, including water towers.
The optimal solution for the cottage village is the use of a pumping station, combining several units in one installation. In such a system, it is not necessary to use water storage tanks.
The implementation of the water supply project for the cottage village begins with the design of a package of initial permits. Its main parts are:
- technical conditions;
- technical task;
- connection conditions.
After approval and approval by the appropriate authorities of the technical specifications, you can proceed directly to the design.
At the initial stage, initial data are collected: the features of the location of the village, the number of future consumers, the volume of future work, etc. are studied.
At the second stage, a working draft is prepared to be approved. Further, on the basis of the completed technical specifications, the project of the cottage village is carried out directly.
The final step is to create blueprints for handing over to the construction team.
Water supply of the cottage village from the well
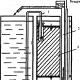
If the water supply to the cottage village is planned by pumping from the well, in this case, the best option would be to perform a water intake unit. It consists of:
- three-phase industrial submersible pumps;
- water meters;
- large storage tanks for collecting clean water for household and fire needs;
- secondary water lift pumps;
- automation devices.
The use of powerful industrial units of 10 to 20 cubic meters can lead to unpleasant consequences: the inclusion of such a pump creates a water hammer, which significantly reduces the resources of its engine. This may cause damage to the downhole filters. To avoid this, it is necessary to ensure a smooth start-up of the pump. And to reduce the frequency of its switching on, large tanks for collecting water are used, equipped with pumps of the second rise.
If it is not possible to install large water tanks, a frequency converter can be used. Its main function is to adjust the speed of the pump motor. The frequency converter lowers the pump voltage if the water flow is low and the pump may not work at full strength. And vice versa - with a large consumption of water, the pump starts to work at the highest speeds.
A frequency converter is provided for each pump. If for some reason one unit does not work, then a signal is sent from the frequency converter to the second pump, and it is connected to the operation of the first device.
Autonomous water supply cottage village
The water supply of the autonomous type cottage community is the supply of each house with its own well and the laying of a separate water supply.
Organization of autonomous water supply begins with the creation of a source of water: a well or a well. The best option for providing water to a large house is to drill an artesian well with a depth of 100 meters or more.
In order to supply water to the house, it is necessary to install submersible pumpas well as a hydraulic unit. The latter serves to collect pumped water and monitor the operation of the unit. When a certain pressure is reached, the pump is switched off, and at the moment of pressure drop it starts functioning.
Description:
When houses are built on an individual basis, neighbors rarely manage to organize the drilling and maintenance of a collective artesian well. More often than not, each owner himself deals with water supply and water treatment. Moreover, he faces a difficult choice.
Water for cottage villages and houses
Whatever method of water supply the owner of the cottage chooses, he will usually have to equip his water treatment system. Even if he manages to connect to the water supply, all the same, the quality of the water is unlikely to “satisfy” the water heater and autonomous heating equipment. Especially if these are imported devices that are very sensitive to the composition of water.
But more often, owners of private houses, as well as the owners of small enterprises in the suburbs, prefer to drill wells. They are collective and individual, artesian and sand. Collective wells are usually drilled during the construction phase of a cottage village. These are always deep wells that can provide consumers with a significant amount of water. The design and licensing of collective wells is usually carried out by the developer. He or the operating organization provides well service and water treatment. Although it happens that along with centralized water treatment, the owners of the cottage also equip their own systems.
When houses are built on an individual basis, neighbors rarely manage to organize the drilling and maintenance of a collective artesian well. More often than not, each owner himself deals with water supply and water treatment. Moreover, he faces a difficult choice.
It is very difficult and expensive to obtain a license for an artesian well, since the sanitary zone, that is, the area on which there should not be any buildings, must be at least 900 m 2, which not every owner has. However, the homeowner has the right to drill a shallow sand well to draw water from the upper aquifer for household purposes. A license is not needed for such a well, although it also has its own sanitary restrictions. But the main problem is that the sand well provides little water, and its quality is poor, therefore, water treatment requires significant costs.
Practice shows that most homeowners are drilling artesian wells, although they are licensed by a few. But in any case, no matter what the well may be, the owner must choose a water treatment system. But understanding the diversity of systems, methods and their effectiveness is not easy for the homeowner. A wide range of equipment is presented on the market, and not only for the private trader, but also for users of collective wells.
Experts told us about the specifics of drilling aquifers and obtaining licenses for them: company representatives shared their experience in organizing water treatment.
Water composition may change.
Is it possible to predict the composition of water before a well is drilled? Does it change over the years? Which wells, sandy or artesian, do the cottage owners prefer? We asked the General Director of RTT JSC to answer these and other questions.
Typically, homeowners “draw” information on the composition of water from their neighbors. The possibilities of scientific forecasting, unfortunately, are limited, because the cadastres reflect old data (until the early 1990s) on well drilling in the Moscow Region and studies of the chemical composition of groundwater. This does not mean that now he is the same. In our practice, and we have been drilling wells since 1993, there have been cases when the composition of water has changed significantly in the well over 7 years. This is due to changes in the total composition of water throughout the horizon.
So, it makes no sense to buy long-term expensive equipment for water treatment, since it may be necessary to completely replace it with a new composition of water?
Personally, I do not share this opinion. In about 10% of cases, the composition of water can change on average over 10-15 years. But with short-lived equipment there will be many problems even for a short period of time.
"Beach" in the Moscow region - high iron content. In our experience, this problem is typical for approximately 70% of water sources. It may happen that the iron was normal or almost normal, and then its content increased sharply. This is due to a change in the nutrition area of \u200b\u200bthe aquifer, when sediment infiltration occurs through buried peaty soils. The second problem of the Moscow Region is the increased water hardness.
Are homeowners still more likely to order sand wells or artesian? What is their average depth in the suburbs?
In the Moscow Region, the average depth of sand wells is 18 m, of artesian wells - 80 m. Nowadays, artesian wells are more often ordered, since they practically do not build small houses. Typically, cottages are built with an area of \u200b\u200bmore than 200 m 2 with three to four points of water analysis. They require about 2.5–3 m 3 of water per hour — only an artesian well will provide such a volume. Sandy gives up to one 1 m 3 / h.
What is the percentage of individual and collective aquifers?
Our company deals only with individual wells. But according to the volume of centralized construction of cottage villages in the suburbs (usually construction companies drill collective wells), it can be judged that this is not more than 10% of the total number of wells. Individual developers have to drill their own well, as neighbors, as a rule, are already provided with water sources. For example, take garden cooperatives. In Soviet times, they were not allowed to build permanent housing there, and the water supply system, if built, was only summer. Now they are building capital houses in summer cottages, this is allowed. And there is nothing left but to drill your wells.
Is it difficult to apply for a well? Who is solving this problem?
For collective wells - a construction organization. For personal - the owners themselves. Obtaining a license for an artesian well is quite difficult. The owner must provide a sanitary zone around the well (at least 30 x 30 m). For sand wells drilled into the upper aquifers, it is required to maintain a distance from the septic tank of at least 30 m. But here in exceptional cases it is possible to coordinate a shorter distance than required by the norm.
If we look at the situation throughout Russia, we will see a massive violation of sanitary standards. There are practically no septic tanks in the villages, instead of them there are cesspools. And water is used without any preparation at all ...
It may happen that according to the cards the water should be in a certain place, but in fact it is not there?
In the suburbs it is very rare that there is no water even at great depths. As an unpleasant surprise, you can probably get very poor quality water. Because of this, there will be too many problems with cleaning and water treatment.
Well Licenses
The cost of water treatment depends on the quality of water, which, in turn, is tied to many factors. What aquifers occur in the Moscow region? What impurities are characteristic for them? What needs to be done to license an artesian well? We asked to answer these and other questions Andrey Mironenko, Head of the Department of Geology and Licensing in Moscow and the Moscow Region, Department of Subsoil Use in the Central Federal District.
In accordance with the law of the Russian Federation “On Subsoil”, for drilling an artesian well, it is necessary to obtain a license for the right to use subsoil. The license is issued not for a well, but for a subsoil plot that has a certain area on the surface of the earth. Accordingly, the applicant must submit a certificate of ownership of land or a lease of land. This is the first.
Further, it is necessary to determine: how much water is needed, what quality, for what purposes, i.e., to calculate water consumption according to the approved standards and coordinate it in the department of water resources in the Moscow region of the Moscow-Oka basin water department of the Federal Agency for Water Resources.
Then you need to get the conclusion of Rospotrebnadzor on the suitability of this land for the organization of the sanitary protection zone of 1 well belt. For an artesian well, in accordance with the requirements of SanPiN 2.1.4.1110–02, the size of the sanitary protection zone 1 of the well’s belt is 60 x 60 m. This section should be fenced, there should be no buildings on it. In exceptional cases, Rospotrebnadzor may agree to reduce the sanitary protection zone, however, it cannot be less than 30 x 30 m.
Then you need to get an opinion on the design of the well in the territorial Center for State Monitoring of the State of the bowels of the Federal State Unitary Enterprise “Geocenter-Moscow”. Based on the required volumes of water, the intended purpose and the hydrogeological conditions of the area, experts will determine what aquifer and depth the well needs to be drilled. In conclusion, there is a geological section, it is indicated at what depth aquifers lie, what is their thickness and water availability. The expected chemical composition of the water is also indicated.
After obtaining a license for the right to use subsoil, the customer turns to a specialized organization, where they draw up a project for drilling a well and coordinate it in the prescribed manner. When a well is drilled, it should be put into operation - for which a commission on state acceptance is created. It is necessary to obtain an opinion from Rospotrebnadzor on the quality of groundwater and the possibility of their use for domestic and drinking water supply. Next, the well should be put on state accounting, equipped with a sanitary protection zone, and a report should be submitted to the state geological examination with an assessment of the operational reserves of groundwater.
All approvals, state registration and assessment of groundwater exploitation reserves will require, of course, considerable costs.
Apparently, the owners of collective wells go such a difficult path?
Of course, but not only them. Owners of private land who do not want to break the law draw up all these documents.
Are there sanitary requirements for water quality?
In accordance with SanPiN 2.1.4.1074-01, it is necessary to determine the presence of more than 40 components in water using three types of analysis: chemical, bacteriological and radiological. Such analyzes began to be done over the past few years, and it turned out that the water of some of the wells did not comply with radiation safety standards (NRB-99). They also found that in some aquifers the MPCs of lithium, strontium, fluorine, and other elements were exceeded.
The most widely used in the Moscow region for water supply is the Podolsk-Shcholkovsky aquifer. The water quality in it almost always corresponds to SanPiN 2.1.4.1074–01, with the exception of the iron content. The underlying Aleksin-Protvinsky aquifer is also actively exploited, but in this water there is often an increased content of fluorine, strontium and lithium, and therefore it is necessary to incur large costs for water treatment. But if, say, an enterprise needs a very large volume of water, it cannot get it only from the Podolino-Bolkovsky horizon, so an additional deeper well will have to be drilled.
Doesn't the chemical composition change over the years?
Of course, it is changing - there is water pollution, since there are many industrial enterprises in the region, many treatment facilities that work inefficiently, discharging wastewater onto terrain and into water bodies. In addition, after so many years of restructuring, hundreds of abandoned artesian wells remained, which are sources of groundwater pollution. Currently, in the territories of large regional centers and in their environs, the problem of groundwater quality is becoming the most urgent.
Are there any features for licensing sand wells?
According to Art. 19 of the RF Law “On Subsoil”, a license is not required for drilling a well on the first aquifer from the surface if the horizon is not used for centralized water supply. The compliance of the subsoil plots with the specified conditions for each specific region is established by the Rosnedr territorial divisions together with state authorities of the constituent entities of the Federation. The arrangement and operation of wells on the first aquifer that is not used for centralized water supply is carried out in the manner established by the executive authorities of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation.
There is a dual interpretation of the law. Previously, the law of the Moscow Region On Subsoil and Subsoil Use in the Moscow Region was in force (repealed by Law No. 88/2005 – OZ of 03/10/2005), which allowed underground water to be used only for the personal needs of the owner of the land. That is, for others, for example, for commercial purposes, a license was required. The federal law does not say anything about this. Although the law of the Moscow Region has been repealed and the new rules have not been established, the regulatory authorities still insist that a license is needed if water is used for commercial purposes. The logic is this: since everyone pays for water, why can merchants who use it in hotels or car washes use water for free? Therefore, businessmen are fined by both the police and Rosprirodnadzor.
What sanitary requirements exist for sand wells?
The same as for the wells. According to SanPiN 2.1.4.1175–02, washing vehicles, watering animals and other activities that contribute to water pollution are not allowed in a radius of 20 m. The place should be chosen in an unpolluted area, remote from cesspools, toilets, fertilizer depots, sewer facilities and other sources of pollution at least 50 m above the groundwater flow.
But to provide such conditions in the garden is almost impossible ....
Of course, impossible. You can be responsible for yourself, and what a neighbor will build within 50 m on his site is only his business. Therefore, in many settlements, the first aquifer from the surface is contaminated with nitrites, nitrates, oil products and other substances of technogenic origin.
But if we talk about violations, they are more characteristic of cottage villages, where homeowners, without a license, drill artesian wells that do not meet sanitary requirements, which leads to pollution of the main exploited aquifers.
| Larisa Fadeeva |
Larisa Fadeeva, leading specialist of the department of state control and supervision in the field of subsoil use of Rosprirodnadzor Checks of subsoil users (mainly legal entities) for their licenses are carried out in accordance with the annual plan. Sometimes, in the event of a complaint, we leave for an unscheduled inspection. It happens that businessmen, instead of one deep well, drill several shallow ones and supply hotels, pools and other facilities with water. This is done so as not to issue a license and not to pay for water. So they interpret the law, which does not require a license when using the water of the first aquifer for personal needs. But in this case, the water is not used for watering the garden or watering livestock, but for commercial purposes. Of several small wells, it is consumed more than bona fide entrepreneurs take from one artesian well. We believe that in such cases, businessmen should apply for a license and pay for water, as all individuals and legal entities do. |
Water treatment. Multimedia download aeration type system
The water treatment process always starts with a water analysis. Usually 23 indicators are used, but sometimes an extended analysis is required - by 40 indicators. Although today about 2,000 impurities that may be contained in water have been studied, the same amount of probably there can be inclusions that have not yet been studied ...
But if we talk about the water near Moscow, then the most characteristic impurities are a high content of calcium and magnesium (hardness salts) and a high content of iron. Also in the water there may be an increased or insufficient amount of fluorine, impurities of hydrogen sulfide, ammonium and petroleum products may be contained. Well and, of course, mechanical and organic pollution are characteristic.
There are methods that recommend using certain types of filter media for a given water composition. However, working according to a “template”, that is, according to a certain standard, does not always give the desired effect. When selecting equipment for a particular object, it is necessary to carefully study the composition of water, all its indicators, since some chemical inclusions can impede the work of the most seemingly effective filter media. The use of multimedia filter media (both in the deferrization block and in the softening block), capable of differentially tracking and leveling “excess” chemical compounds in the water composition, gives a good result. As a result, complex removal of many negative organic and inorganic inclusions can be achieved. It is still important not to concentrate on certain brands, but to select the most effective equipment for a given facility.
But let's start in order. First of all, water requires mechanical cleaning. Our experience has shown that of the three types of common filters (mesh, disk and cartridge), disk filters are the most effective. Such a filter combines the advantages of mesh and volumetric filtration, is easily washed and has an unlimited service life.
Removal of iron, manganese and hydrogen sulfide is possible using reagent filter media with regeneration with a solution of potassium permanganate. In the process of a chemical reaction, iron, which is in a divalent dissolved state, is deposited on the filter loading layer. When washing the filters, the sediment and a less concentrated solution of potassium permanganate is discharged into the local sewage system and eventually gets on the ground, which negatively affects the environment and also interferes with the effective operation of biological treatment plants. In addition, it is unsafe for humans, if during the regeneration period of the filters there will be unauthorized analysis of water.
Alternative possibilities for removing dissolved iron in water and blowing hydrogen sulfide provide reagent-free aeration-type systems. Using a compressor, water is preliminarily saturated with atmospheric oxygen, which enters the filter charge and in the presence of which the oxidation process is more efficient. The use of such systems eliminates environmental pollution. In addition, in the process of aeration, water conditioning occurs, which positively affects its quality.
The next stage of water treatment is water softening, i.e. neutralization of calcium and magnesium salts. Such systems do not differ in a wide variety, although there are, for example, magnetic transducers that are installed directly on the pipe. They magnetize water, preventing crystallization and the deposition of hardness salts. The chemical composition of the water does not change. We believe that it is more efficient to use the traditional method of water softening using ion-exchange resins as part of the downloads. An additional effect is the use of multimedia ion-exchange resins of selective action. For example, if the water has a high concentration of dissolved iron and at the same time it is necessary to remove ammonium impurities, heavy metal ions, humic substances, and aluminum.
It is also justified to include a cartridge charcoal filter in the equipment, which has the function of a sorption filter and is able to prevent the chips of the filter load from entering the water circuit.
To disinfect water, we put an ultraviolet sterilizer as an element of water treatment. This is necessary if there is a risk of water contamination, confirmed by laboratory tests, especially if water is taken from a well or shallow wells.
Some types of hazardous inclusions can only be filtered using reverse osmosis systems. As a rule, such a system is installed on a line of water intended only for drinking and cooking. These devices are quite conservative, but they can be supplemented, for example, with a mineralizer to saturate water with certain doses of substances necessary for health.
Some companies try to impose an excessive set of equipment without explaining to the customer that there are more optimal inexpensive options for a water treatment system. There are companies that offer a full range of systematic after-sales service. We are trying to install such water treatment systems that have optimal functions for this facility and generally do not require service. Or, at least, we try to minimize the worries of the cottage owner about the water entering the house.
Integrated water softener
In the water treatment market, softeners with monodisperse gel strongly acidic cation exchange resins of leading world manufacturers are currently used. Such resins have extreme chemical and mechanical resistance, high exchange capacity. These are reliable filters that perform one function well - water softening.
However, for an individual user when there is no centralized water purification system, as a rule, it is necessary to solve the problems of eliminating several types of pollution. An integrated system perfectly copes with such cleaning. The loading uses a mixture of resins, which allows you to remove hardness salts, and iron, and manganese in one bottle. Therefore, the system of integrated water treatment, in my opinion, can be considered the most effective filter.
Water treatment. Pressureless aeration systems
In cottage villages where water is intended for a large number of consumers, there are two ways to approach the issue of water treatment. You can put an individual system in each house - before this method was very common. But in the last two to three years they began to actively establish water treatment systemsserving the whole village.
This allows not only to reduce the cost of water treatment for each homeowner, but also to centrally solve the problem of effluents, as well as to increase the degree of reliability and resolve issues with regulatory authorities.
In recent years, the state has begun to pursue a focused policy on subsoil use issues. All wells, including individual ones, must be licensed. If there is no common well in the village, then each has its own drilled. This is well understood by the controlling authorities, who come with inspections. Which pushes homeowners to organize collective water intake and water treatment systems.
In the Moscow region, the most common “standard” set of pollution. As a rule, water in a common well is cleaned of iron and hydrogen sulfide. Water hardness in the Moscow region is usually within 10 mEq / l. Although the indicators are rather big, such rigidity can be agreed upon with regulatory authorities. And who wants to improve the water, put in their cottages installations for water softening. Such a scheme (general deferrization and individual softening) is optimal, since not all homeowners agree to bear the operating costs of water softening. Many people prefer to solve this problem themselves. As for iron, very often it is many times higher than sanitary standards. In addition, water can be ironized by one-time capital investments at no additional cost.
This is how the non-pressure aeration system works, which our company supplies to the market. It allows you to remove iron from water without using catalytic charges. In general, there are different methods for this, for example, reagent, which is almost never used in the Moscow region. Now reagentless methods are widely presented on the market, but most often they involve the use of pressure aeration with catalytic loading. The method is effective, but the catalytic load, most often, lasts no more than two or three years, then they need to be changed. And if there is hydrogen sulfide in the water, then the service life is even less.
The principle of operation of our system is the same as the schemes with pressure aeration, only here the saturation of water with oxygen occurs through dispersing-distribution nodes (DRU). The design of the nodes is such that the water flow is crushed into small drops. As a result, the contact surface of air and water, and hence the saturation of water with air, is greater than with pressure aeration, when air is supplied to the water layer by a compressor (similar to air supply to water in aquariums). Due to the intensive process of saturation of water with oxygen in the DRU, the oxidation of iron dissolved in water is significantly accelerated. Then the water enters the storage tank, and from it, using the pumping station, is supplied to the sedimentary filter system. In the first block, dissolved iron is oxidized to undissolved, and then sedimentary filters collect it. In automatic mode, the regeneration mode is periodically turned on: by the reverse current of water, the accumulated iron is washed off into the sewer.
The advantage of such a system is that it completely copes with the oxidation process, without the use of catalytic charges. It is enough to apply sedimentary loading. For example, we use an inert loading, which does not add unnecessary components to the water and has a low percentage of abrasion - it can work without reloading for more than 10 years.
Our installation is slightly more expensive in terms of capital costs compared to a pressure aeration installation, but it benefits in performance. I already mentioned the reason - in pressure aeration systems it is necessary to restart the catalytic loading. Reloading is a time-consuming process, often the upper catalyst layer is “sintering”, it has to be broken by some mechanical devices (scrap, etc.), which leads to breakdowns of the central distribution pipe or filter neck. Such systems can be chosen by developers who are not involved in servicing villages. And for operators, our system is preferable.
| ... |
Sergey Ruzhinsky, chief engineer of AT Water Systems I think free-flow aeration is more suitable for deferrization in cases where small amounts of water are consumed. In such systems, it is efficient to use a large storage tank. But in any case, the dimensions of the tank are limited. It is rather problematic to provide a large area of \u200b\u200bcontact of water with air for large volumes of water. If water is sprayed into the tank, I would not call such a system gravity aeration, since water still comes under pressure. We use a reagentless pressure aeration system using compressors and catalysts. With small volumes of water consumption, we can offer an ejector. The policy of our company is based on providing the customer with as much information as possible about the possible water treatment systems and prices for each installation. So that the client can make a choice (including being limited to the most necessary), taking into account the composition of water, the volume of its consumption and its financial capabilities. Victor Kiselev, Head of Water Treatment Department, BIICS Indeed, the iron removal step is the most difficult. This is caused, on the one hand, by the variety of forms of the presence of iron in water (divalent, trivalent, colloidal, organic, bacterial), on the other hand, by the absence of one universal method for their removal and the corresponding equipment. We prefer pressure aeration systems with a compressor, followed by catalytic oxidation of iron on a filter medium. We also use non-pressure aeration systems using ejectors of different capacities. In some cases, we turn to a time-tested method for removing iron using potassium permanganate. Pavel Sidorov, manager of the water treatment department of the company "Resource" If the iron content in water is higher than 1.5 mg / l, we use reagent deferrization methods: using sodium hypochloride and potassium permanganate. This is a reliable, long-proven way to remove iron. With a lower percentage of iron in water, we use pressure aeration systems using a compressor and catalytic loading. We use non-pressure aeration systems (using water sprayers or containers with a large contact surface of water and air) only with a small iron content in the water. |
The number of water lines should be taken taking into account the category of water supply system and the priority of construction.
When laying pipelines in two or more lines, the need for switching between pipelines is determined depending on the number of independent water intake structures or pipelines supplying water to the consumer, and in the event of a shutdown of one piping or its section, the total water supply to the facility for drinking and drinking needs to be reduced no more than 30% of the estimated consumption, for production needs - according to the emergency schedule.
When laying a water conduit in one line and supplying water from one source, the volume of water must be provided for the time the accident at the water conduit is liquidated in accordance with clause 9.6. When supplying water from several sources, the emergency volume of water can be reduced.
Water networks should be circular. Dead-end water supply lines may be used:
for supplying water for industrial needs - if the interruption in water supply is permissible for the period of liquidation of the accident;
for supplying water for domestic and drinking needs - with a pipe diameter of not more than 100 mm;
for supplying water for fire-fighting or for household-fire-fighting needs, regardless of the water flow for fire fighting - with a line length of not more than 200 m.
Ringing of external water supply networks by internal water supply networks of buildings and structures is not allowed.
Note. In settlements with a population of up to 5 thousand people. and water consumption for external fire extinguishing of up to 10 l / s or with the number of internal fire hydrants in a rank of up to 12 dead-end lines with a length of more than 200 m are allowed, provided that fire tanks or reservoirs, a water tower or a counter reservoir at the end of the dead end are installed.
When one section is switched off (between settlement nodes), the total water supply for drinking and other needs along the remaining lines should be at least 70% of the estimated flow rate, and the water supply to the most unfavorable locations of the water intake should be at least 25% of the calculated water flow rate, while free Head must be at least 10 m.
The device of accompanying lines for connecting associated consumers is allowed with a diameter of trunk lines and water conduits of 800 mm or more and a transit flow rate of at least 80% of the total flow rate; for smaller diameters - with justification.
With a width of driveways of more than 20 m, laying of duplicate lines is allowed, excluding the intersection of driveways with inputs.
In these cases, fire hydrants should be installed on accompanying or backup lines.
With the width of the streets within the red lines of 60 m or more, one should also consider the option of laying water supply networks on both sides of the streets.
The connection of drinking water supply networks with water supply networks supplying non-potable water quality is not allowed.
Note. In exceptional cases, in agreement with the bodies of the sanitary-epidemiological service, it is allowed to use household drinking water supply as a reserve for a water supply supplying non-potable water. The design of the jumper in these cases should provide an air gap between the networks and exclude the possibility of reverse water flow.
On water mains and water supply lines, if necessary, the following should be installed:
rotary locks (latches) for allocation of repair sites;
valves for air inlet and outlet when emptying and filling pipelines;
valves for air intake and trapping;
plungers for air discharge during the operation of pipelines;
outlets for water discharge when emptying pipelines;
compensators;
mounting inserts;
check valves or other types of valves of automatic action to turn off repair areas;
pressure regulators;
apparatus for preventing the increase in pressure during hydraulic shocks or in the event of a malfunction of pressure regulators.
On pipelines with a diameter of 800 mm and more, the device of manholes is allowed (for inspection and cleaning of pipes, repair of shut-off and control valves, etc.).
On gravity-pressure pipelines, it is necessary to provide for the installation of discharge chambers or the installation of equipment that protects the pipelines at all possible operating modes from increasing the pressure above the limit acceptable for the adopted type of pipes.
Note. The use of valves instead of butterfly valves is allowed, if necessary, the systematic cleaning of the inner surface of pipelines with special units.
The length of repair sections of water pipes should be taken: when laying water pipes in two or more lines and in the absence of switching - not more than 5 km; in the presence of switching, equal to the length of the sections between switching, but not more than 5 km; when laying pipelines in one line - no more than 3 km.
Note. The division of the water supply network into repair sections should ensure that when one of the sections is switched off, it will turn off no more than five fire hydrants and supply water to consumers who do not allow a break in the water supply.
When substantiating, the length of repair sections of water conduits can be increased.
Automatic operation valves for air inlet and outlet should be provided at elevated critical points of the profile and at the upper boundary points of repair sections of water conduits and network to prevent the formation of a vacuum in the pipeline, the value of which exceeds the permissible value for the adopted type of pipes, as well as to remove air from the pipeline when it filling out.
With a vacuum value not exceeding the permissible value, manual valves can be used.
Instead of automatic action valves for air inlet and outlet, it is allowed to provide automatic action valves for air intake and trapping with hand-operated valves or valves (depending on the flow rate of the removed air).
Plungers should be provided at elevated critical points of the profile on the air collectors. The diameter of the air intake should be taken equal to the diameter of the pipeline, height - 200-500 mm, depending on the diameter of the pipeline.
When substantiating, it is allowed to use air collectors of other sizes.
The diameter of the stop valves that disconnect the plunger from the air intake should be taken equal to the diameter of the plunger connecting pipe.
The required throughput of the ventilation ducts must be determined by calculation or taken equal to 4% of the maximum calculated flow rate of water supplied through the pipeline, counting by the volume of air at normal atmospheric pressure.
If there are several elevated critical points of the profile on the water conduit, then at the second and subsequent points (counting along the direction of the water), the required capacity of the plungers can be assumed to be equal to 1% of the maximum calculated water flow, provided that this critical point is lower than the first or above it no more than 20 mi at a distance from the previous one not more than 1 km.
Note. With a slope of the descending section of the pipeline (after the turning point of the profile) of 0.005 or less, plungers are not provided; with a slope within 0.005-0.01 at the turning point of the profile, instead of the plunger, it is allowed to provide a valve (valve) on the air collector.
8.13.
Water conduits and water supply networks should be designed with a slope of at least 0.001 towards the outlet; with a flat terrain, the slope may be reduced to 0,0005.
Outlets should be provided at lower points of each repair site, as well as at places where water is released from flushing the pipelines.
The diameters of the outlets and air inlet devices should ensure emptying of water conduit or network sections in no more than 2 hours.
The design of the outlets for flushing the pipelines should provide the ability to create in the pipeline the water speed of at least 1.1 maximum design.
As valves on the outlets, butterfly valves must be used.
Note. During hydropneumatic washing, the minimum speed of the mixture (in places of greatest pressure) should be at least 1.2 of the maximum speed of water, water flow rate - 10-25% of the volumetric flow rate of the mixture.
Water discharge from outlets should be provided in the nearest drain, ditch, ravine, etc. If it is not possible to divert all or part of the discharged water by gravity, it is allowed to discharge water into the well with subsequent pumping.
Fire hydrants should be provided along roads at a distance of ns more than 2.5 m from the edge of the carriageway, but no closer than 5 m from the walls of buildings; it is allowed to place hydrants on the roadway. In this case, the installation of hydrants on the branch from the water supply line is not allowed.
The arrangement of fire hydrants on the water supply network should provide fire extinguishing of any mania, structure or part thereof from at least two hydrants with a water consumption for external fire extinguishing of 15 l / s or more and one - with a flow rate of less than 15 l / s, taking into account laying of hose lines with a length not exceeding that specified in clause 9.30 on paved roads.
The distance between the hydrants is determined by the calculation, taking into account the total water flow for fire fighting and the capacity of the installed type of hydrants according to GOST 8220-85 * E.
ECODAR Company has been providing water purification services for water supply systems in cottage and holiday villages Leningrad region and the entire North-West region. We offer a full cycle of services related to water treatment: water analysis in our own accredited laboratory, individual design of a water treatment system, installation, commissioning and maintenance work.
The need for water treatment for rural water supply
Natural water can often be unsuitable for drinking purposes, because according to some indicators, such as hardness, content of iron, fluorides, organic substances, the presence of pathogenic bacteria, they exceed the permissible limits. In addition, anthropogenic pollution is often present in them: heavy metals, organochlorine elements, nitrates, radionuclides, etc. Artesian water is usually used as a source of water supply for country houses. Moreover, often for a number of indicators it does not comply with SanPiN 2.1.4.1074-01 “Drinking water. Hygienic requirements for water quality of centralized drinking water supply systems. Quality control ”, and it must first be cleaned.
Technological methods of water purification
For the water treatment in the water supply systems of country houses in settlements and cottage villages, almost the entire spectrum of technological methods of water treatment is used: aeration, treatment stations, deferrization (reagent and non-reagent), demanganization, ammonia removal, softening, oxidation-sorption method, ultraviolet disinfection, etc. When excessive fluorine, silicon and some other contaminants are detected, membrane filtration is used. A feature of such objects, in particular, is the large daily and seasonal fluctuations in water flow, which should be taken into account when designing, installing storage tanks of the appropriate size or calculating the system for maximum performance.
Stages of organizing a water treatment system
Water analysis. To determine the presence and type of pollutants contained in the water that you plan to use for the water supply of the village, it is first tested for turbidity, color, odor, pH, dry residue, alkalinity, permanganate oxidation and general hardness. The content of nitrites and nitrates, sulfates, chlorides, bicarbonates, hydrogen sulfide and ammonia, fluorides, total iron and dissolved iron, copper, manganese, silicon and other substances is also measured. The composition of the water treatment system in cottages depends on the results of the analysis.
Project development. At the stage of designing the village’s water supply scheme, the type and composition of a suitable water treatment system is determined, taking into account the characteristics of a particular object, the place and method of location of its structural elements are selected. A layout of structural elements of the water supply system is also being developed.
Equipment selection. The choice of water treatment technologies and the determination of appropriate equipment for water supply is carried out on the basis of the results of chemical analysis of water and the study of the technological features of the facility. It is also possible to visit a specialist in order to take a water sample for analysis, clarification of special wishes or installation features.
Delivery. At this stage, transportation of a previously designed and agreed upon set of equipment for water treatment to the facility is carried out at the facility. If the water supply of the village provides for the presence of fragile blocks in the system (measuring equipment and sensors), they are transported in special shock-absorbing packaging.
Mounting. During the installation of the water treatment system equipment, the preliminary installation of the constituent elements is carried out in accordance with the selected scheme. Further, the parts and blocks are interconnected, and then connected to existing communications.
Commissioning. After the direct assembly of the water treatment system, a test run of the entire water supply network is carried out in each cottage of the village. At this stage, the company’s specialists check the compliance of the planned and actual cleaning capacity of the equipment for water supply, as well as the uninterrupted and correct operation of the control equipment. Completion of installation and commissioning of system elements is confirmed by bilateral signing of the acceptance certificate of work performed.
Refine cost
CJSC SPC Gidrogeotech is engaged in engineering surveys in the field of construction. We also carry out geodetic, hydrological work, conduct surveys of underground utilities, and drill engineering and geological wells. The company's specialists are engaged in the search and exploration of mineral deposits and groundwater. Design of water intake units, communications is carried out in accordance with applicable regulatory documents.
The amount of water consumption is calculated from 30,000 rubles. per 1 cubic meter of water per day
The organization and arrangement of water supply for settlements involves the implementation of a number of measures to provide consumers with water resources in accordance with the necessary consumption standards. The main consumers are settlements and industrial enterprises.
Settlements can have different sources of water supply. Surface Sources:
- reservoirs;
- fresh water lakes;
- rivers;
- in some cases, seas.
Underground sources of water supply are also used - these are artesian and groundwater, springs. Water resources can be used for industrial, drinking and fire fighting needs.
What does the water supply system of a settlement consist of
She includes pumping stations first lift, water treatment station, clean water storage tanks, pumping stations of the second lift. Also, the water supply system of villages includes water towers, water conduits and other hydraulic structures.
In the water supply systems of cottage villages, water distribution and main distribution networks are provided for transporting water within the boundaries of the settlement. Depending on the terrain features, underground or ground-based sources of water supply for cottage villages, small and large cities, as well as manufacturing enterprises are used.
The device of the water supply network of the cottage village
External pipelines of the village’s water supply system are divided into several types. Water conduits are the main part of the water supply communications scheme. According to them, water is delivered through the house inlets and central points directly to the consumer.
Water supply for the water supply of the cottage village is located in the driveways on the territory of the settlement rectilinearly or parallel to the building line. Depth of laying should prevent freezing and overheating of water.
Design of water supply for settlements
The most important stage of preparation for the design of water supply systems in settlements is the preparation of initial permissive documentation, which includes the development of technical specifications and technical conditions, justification of connection conditions and the collection of additional data. Actually, design work on the water supply of the village begins after the approval of the terms of reference and approval of the master and cadastral plan.
The main stages of the design of water supply for settlements:
- object study;
- collection of additional information, materials and documentation for a preliminary assessment of the scope of upcoming work, determining the characteristics of technical and technological problems;
- development and approval of a working draft;
- creation of a water supply project for a settlement based on the terms of reference and information collected;
- creation of working drawings for a complex of construction and installation works;
- coordination of design documentation with authorized bodies.
CJSC SPC Gidrogeotech performs the design of water supply to settlements in a quality and timely manner. This is made possible thanks to many years of experience and highly qualified specialists of the company.
Leave a request for design